Abdomen Scan
Overview
Terminology
U/S Whole Abdomen= All abdominal organsU/S Upper Abdomen= All abdominal organs - (Bladder & Reproductive orgs)U/S KUB= Kidneys + Bladder + Reproductive orgs
Echogenicity
Relative echogenicity on ultrasound (high to low):
Darling Parents So Love Kids
(Ref: radiopedia)
Liver
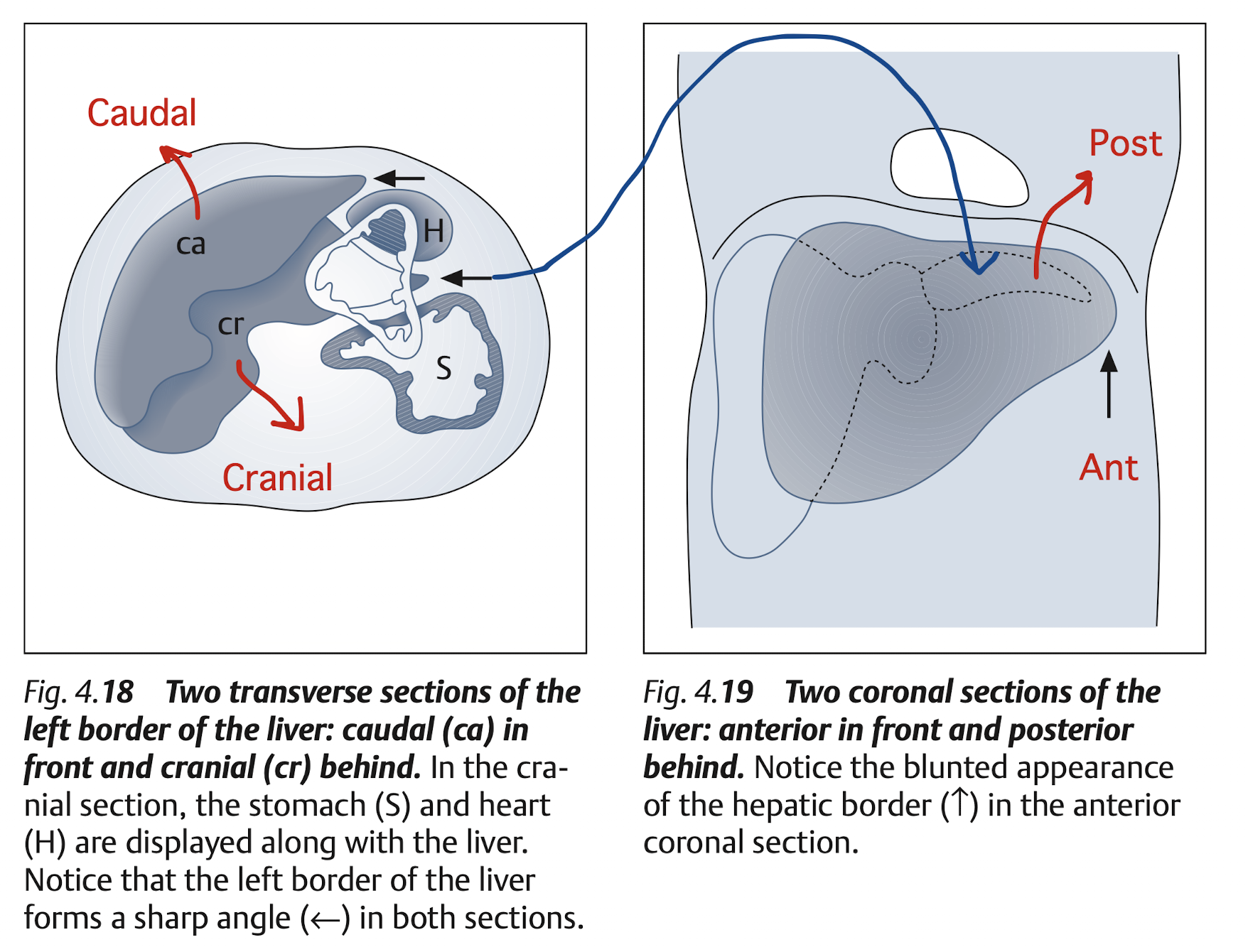
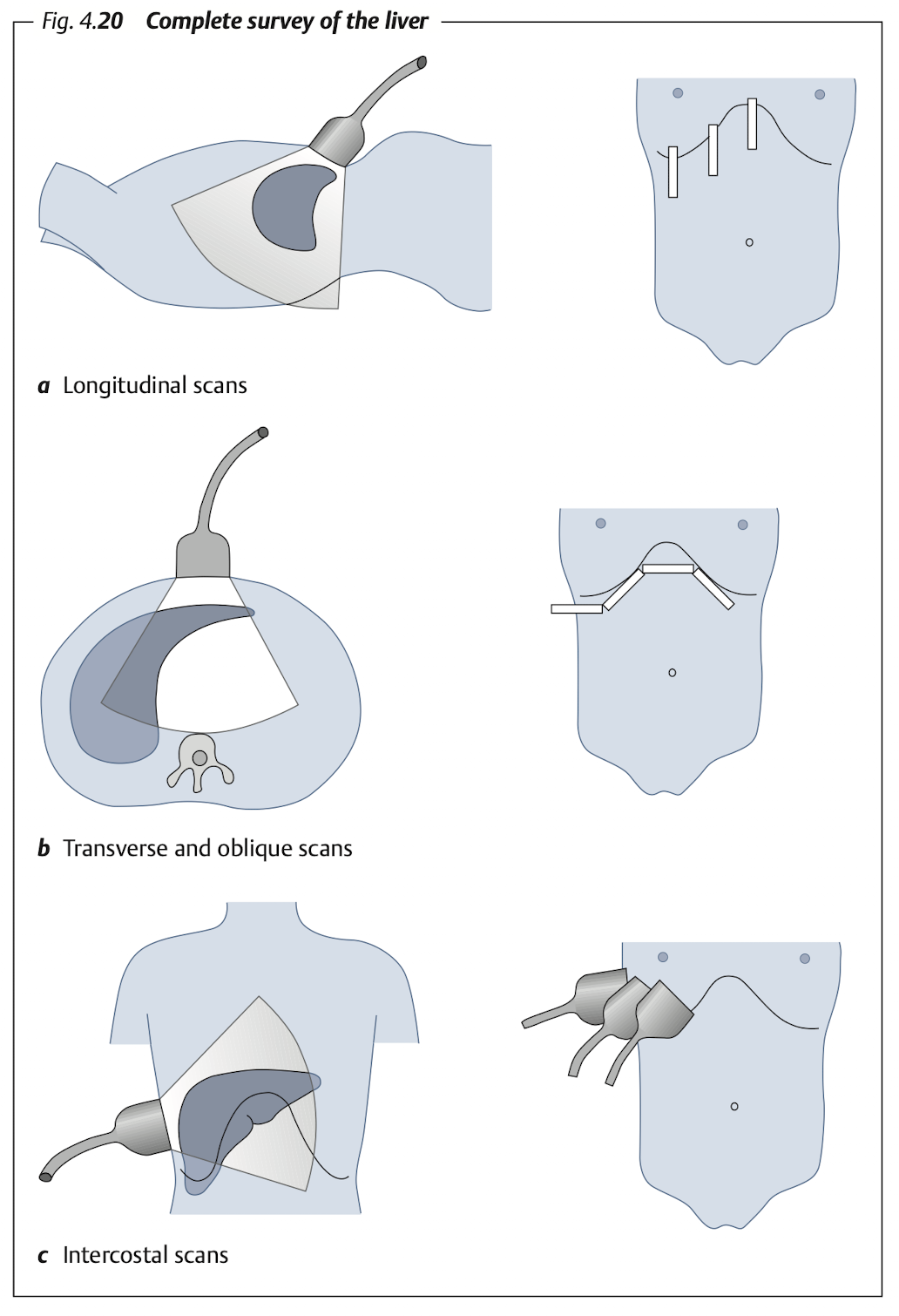
Overview
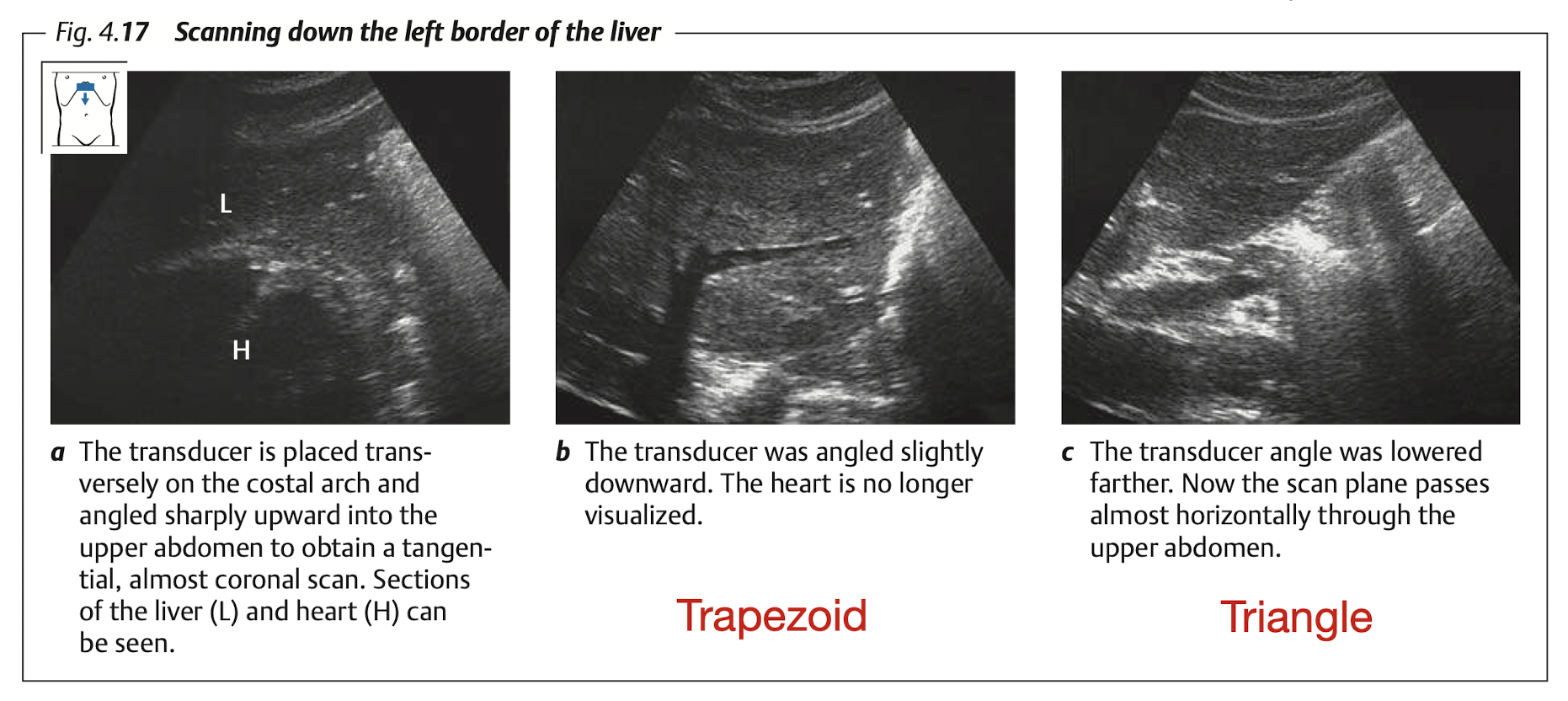
Subcostal: Transverse & longitudinal view of RL & LL (LL must includes caudate lobe)
Intercostal: RL
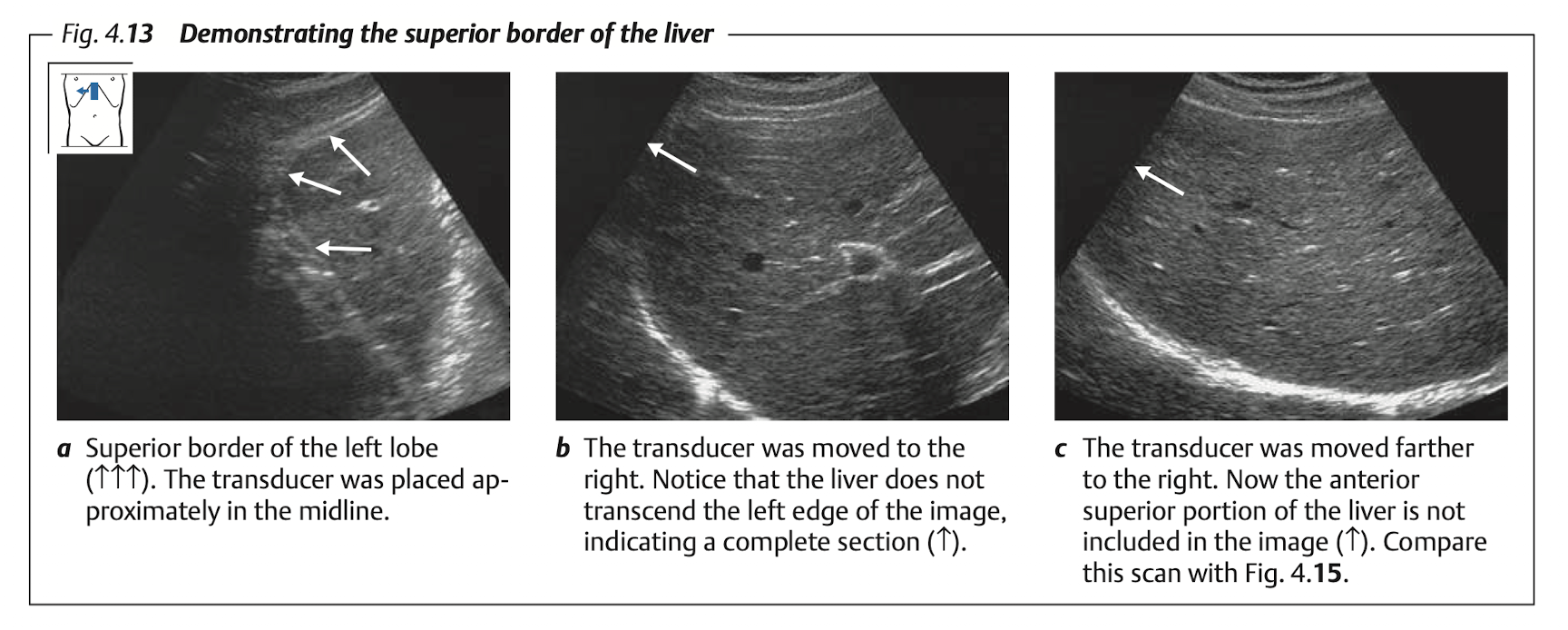
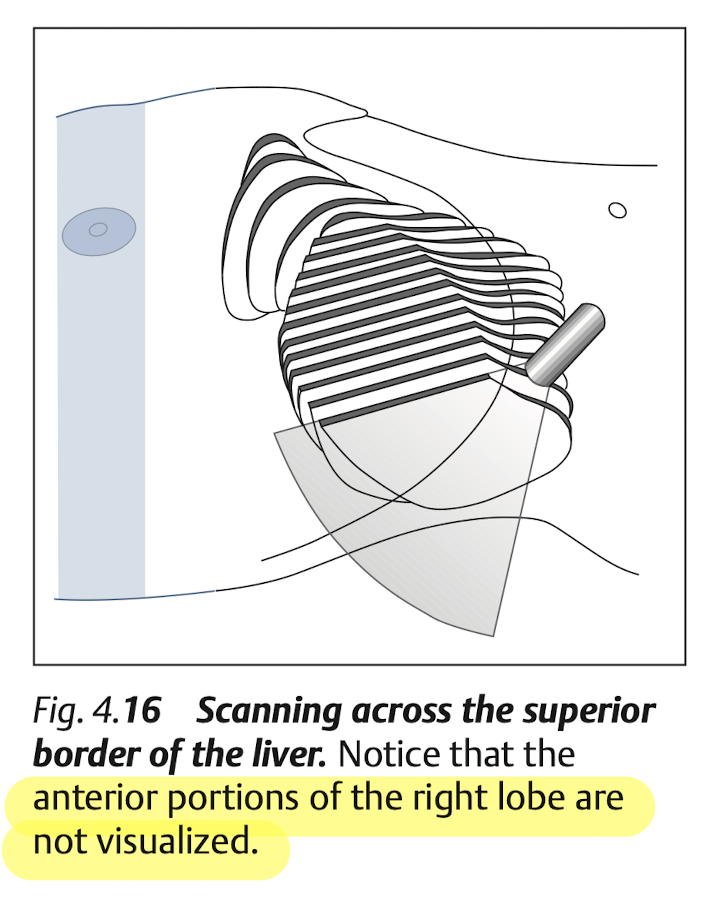
Blind spot of liver at “superior portion of Rt lobe”
Measure
Normal liver span:
15 - 17 cm(sagital, at MCL)Enlarge:
> 15.5 cmHepatomegaly: confident if liver extend to caudal of Rt kidney
(Ref from [2])
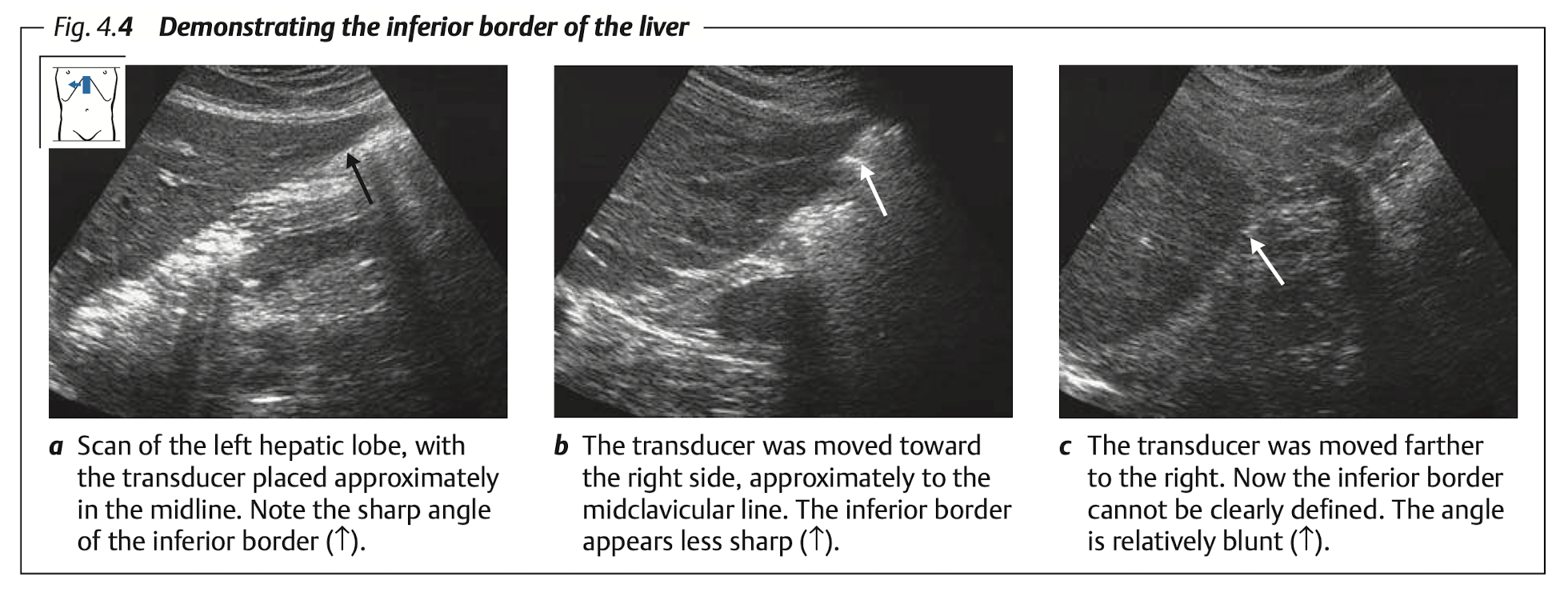
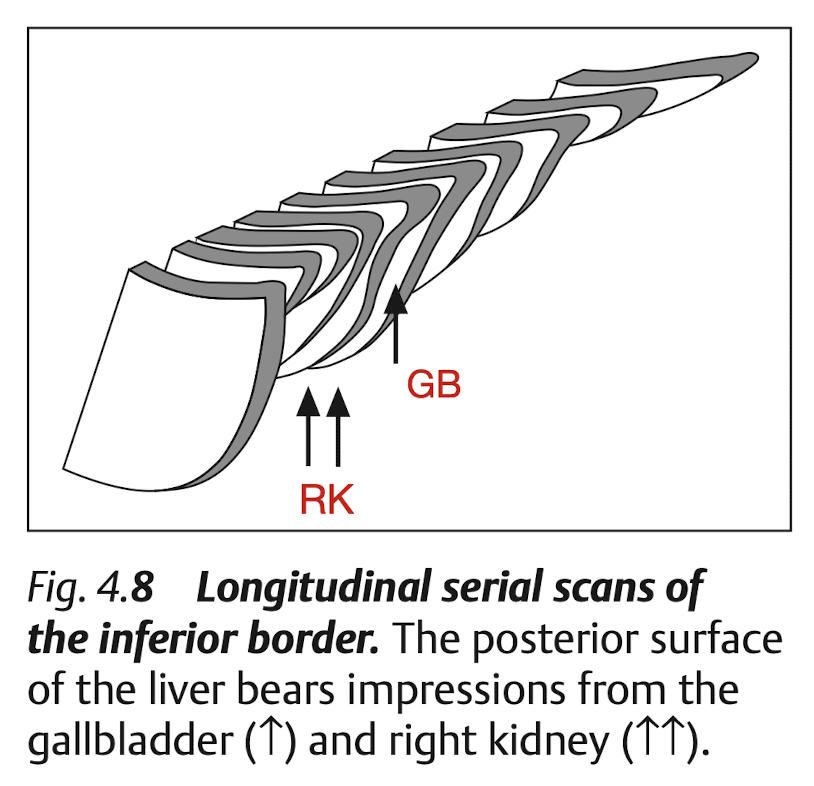
View: Longitudinal
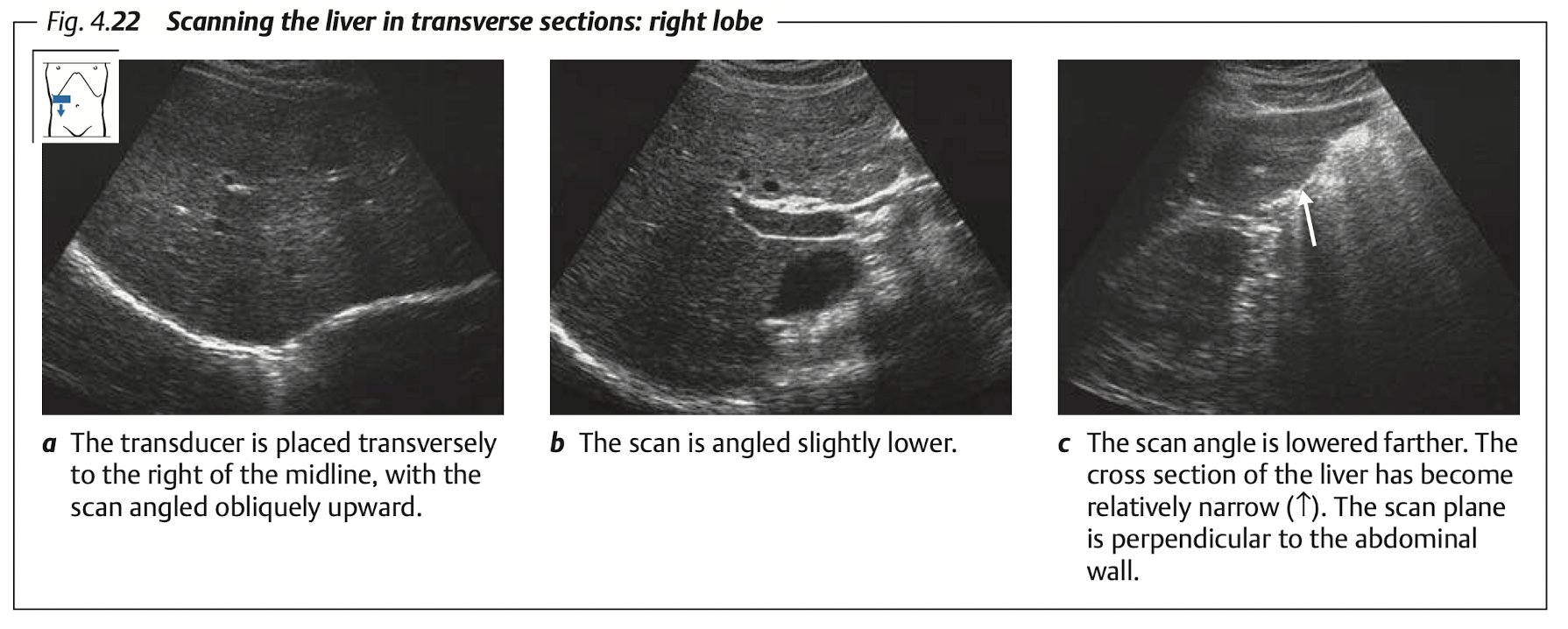
View: Transverse
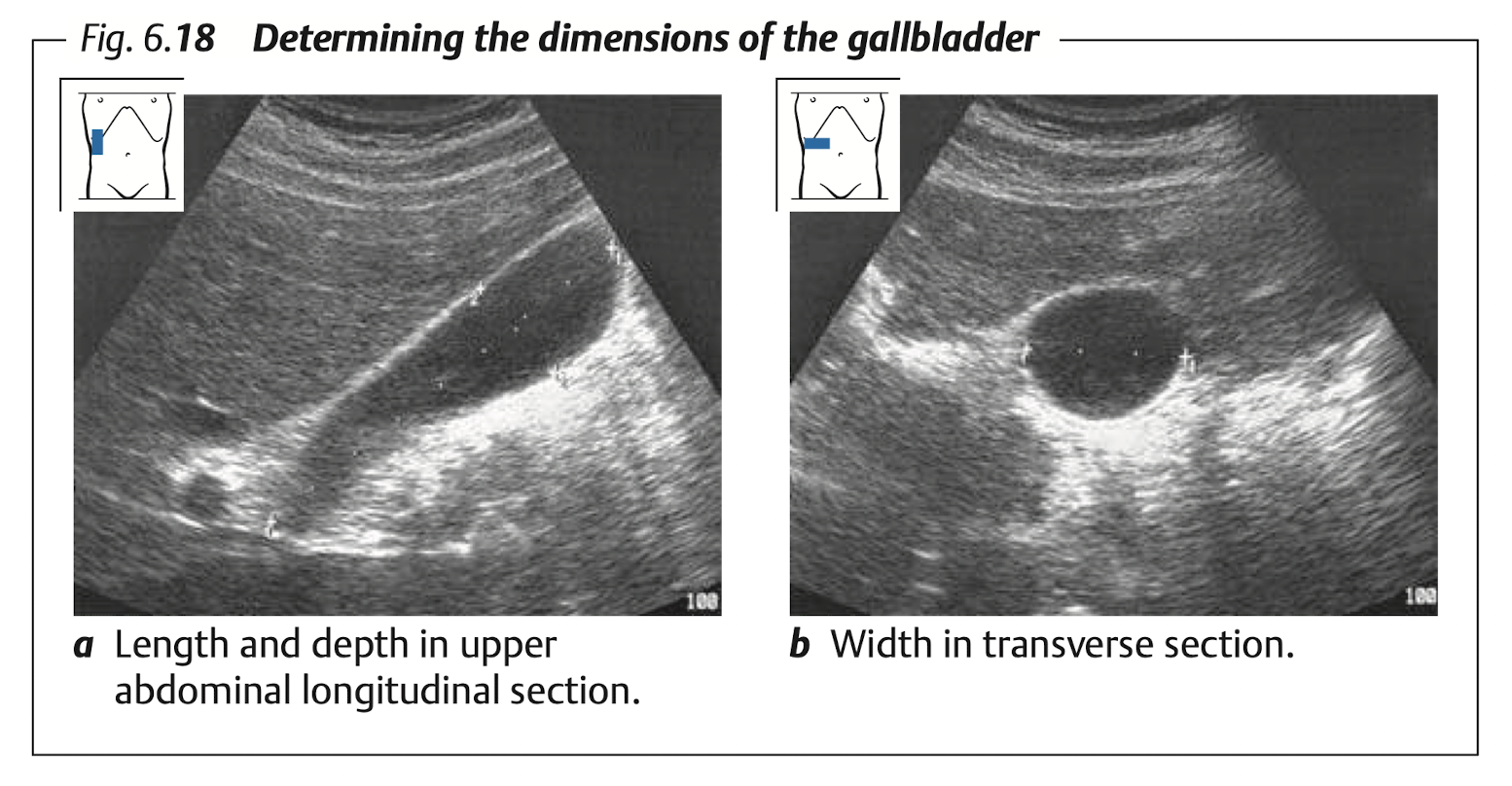
Gallbladder
View: transverse & longitudinal
Measure:
- Diameter: long (9 -
11cm), TV (< 4cm) - Wall thickness at anterior wall in TV section (
< 3mm)
- Diameter: long (9 -
Porta Hepatis
Measure: CBD & PV
CBD
- Measure: internal diameter
< 0.6cm (< 0.9for post-cholecystectomy)- Age > 60 yrs can dilate 0.1 cm / 10 yrs
PV
- Measure: internal diameter
< 13mm - Flow direction:
hepatopetal? (toward liver) orhepatofugal? (away from liver)
View: CBD & PV
View: longitudinal scan (with lt lateral decubitus) to see porta hepatis Figure 10
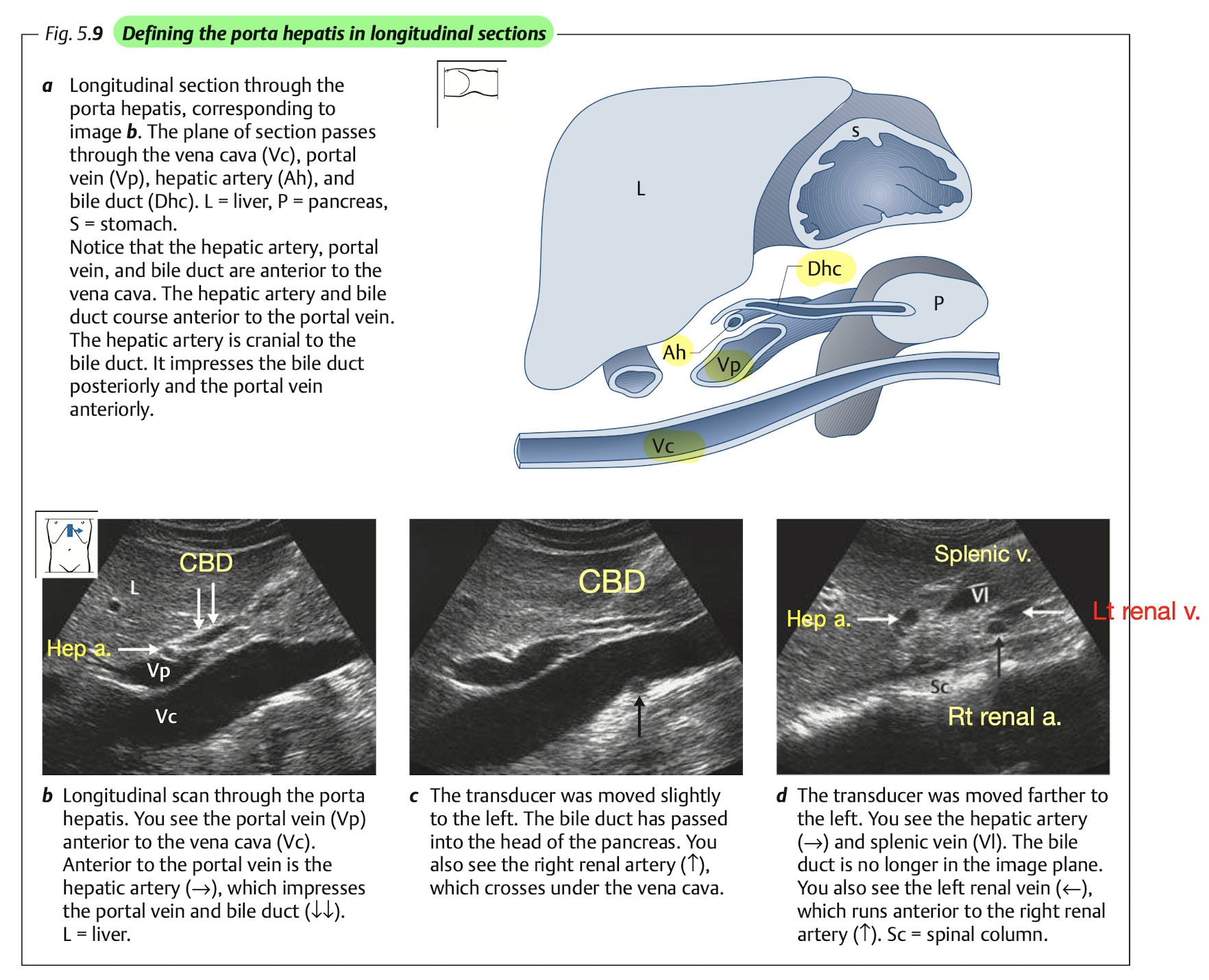
Tips: identifying CBD
- CBD will appear anterior and parellel to PV and IVC.
- Color doppler will show no flow at CBD.
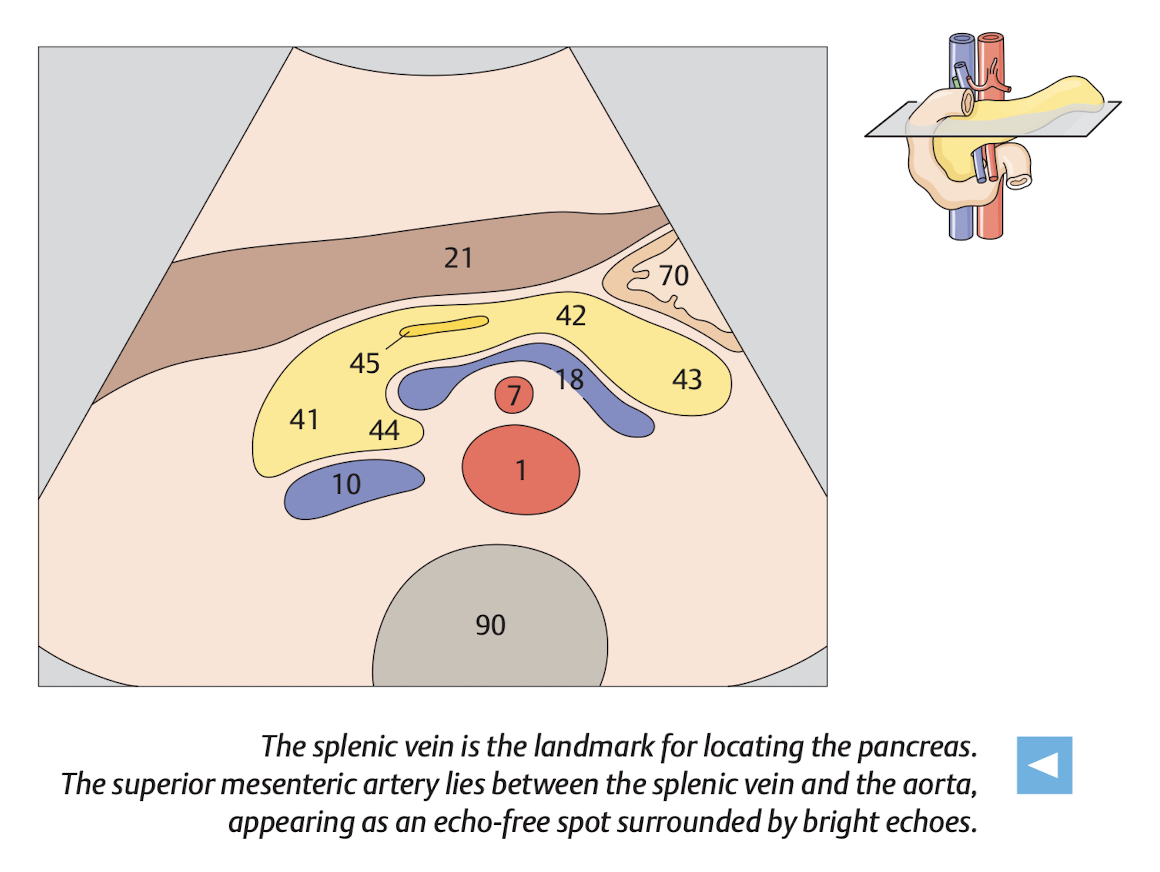
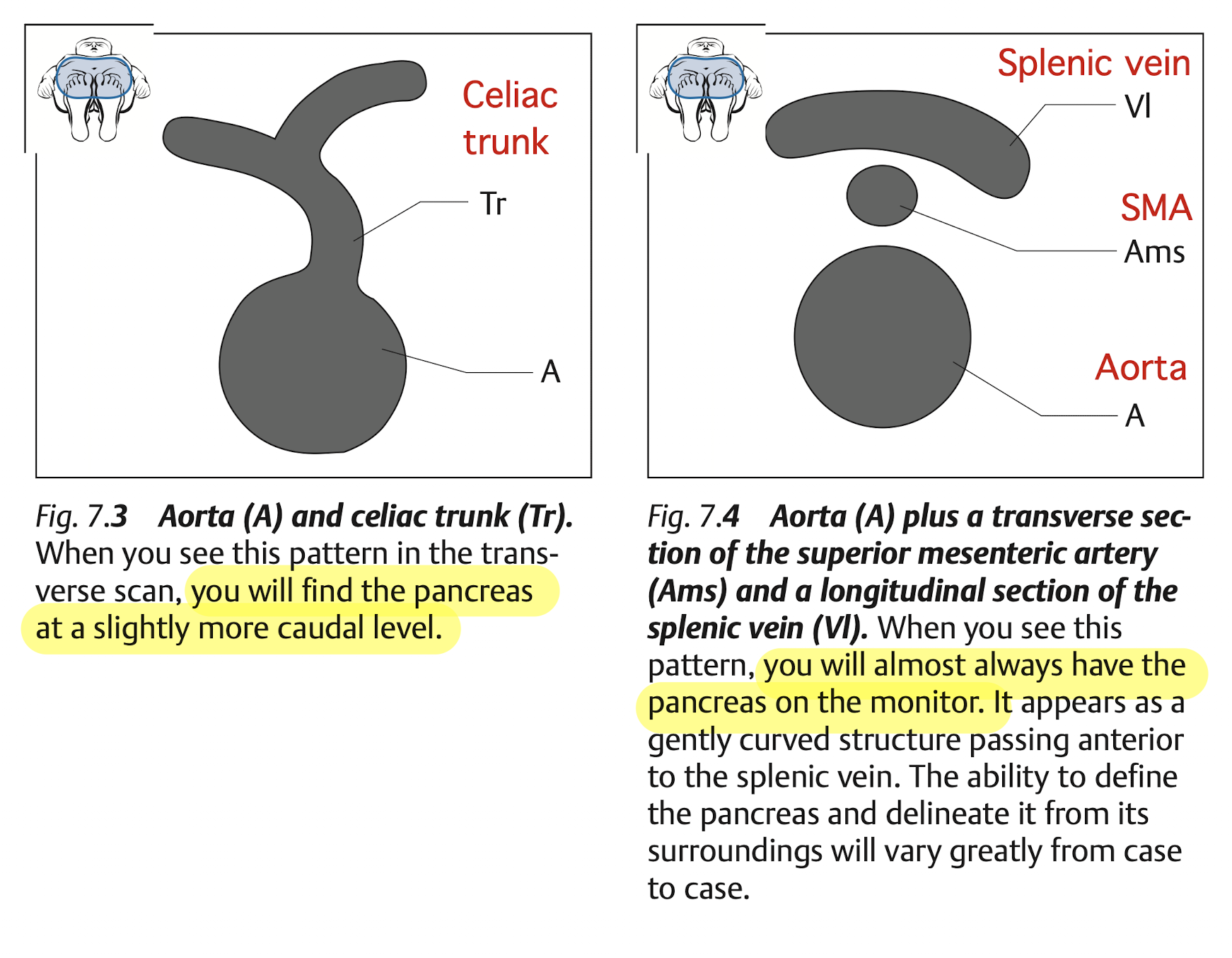
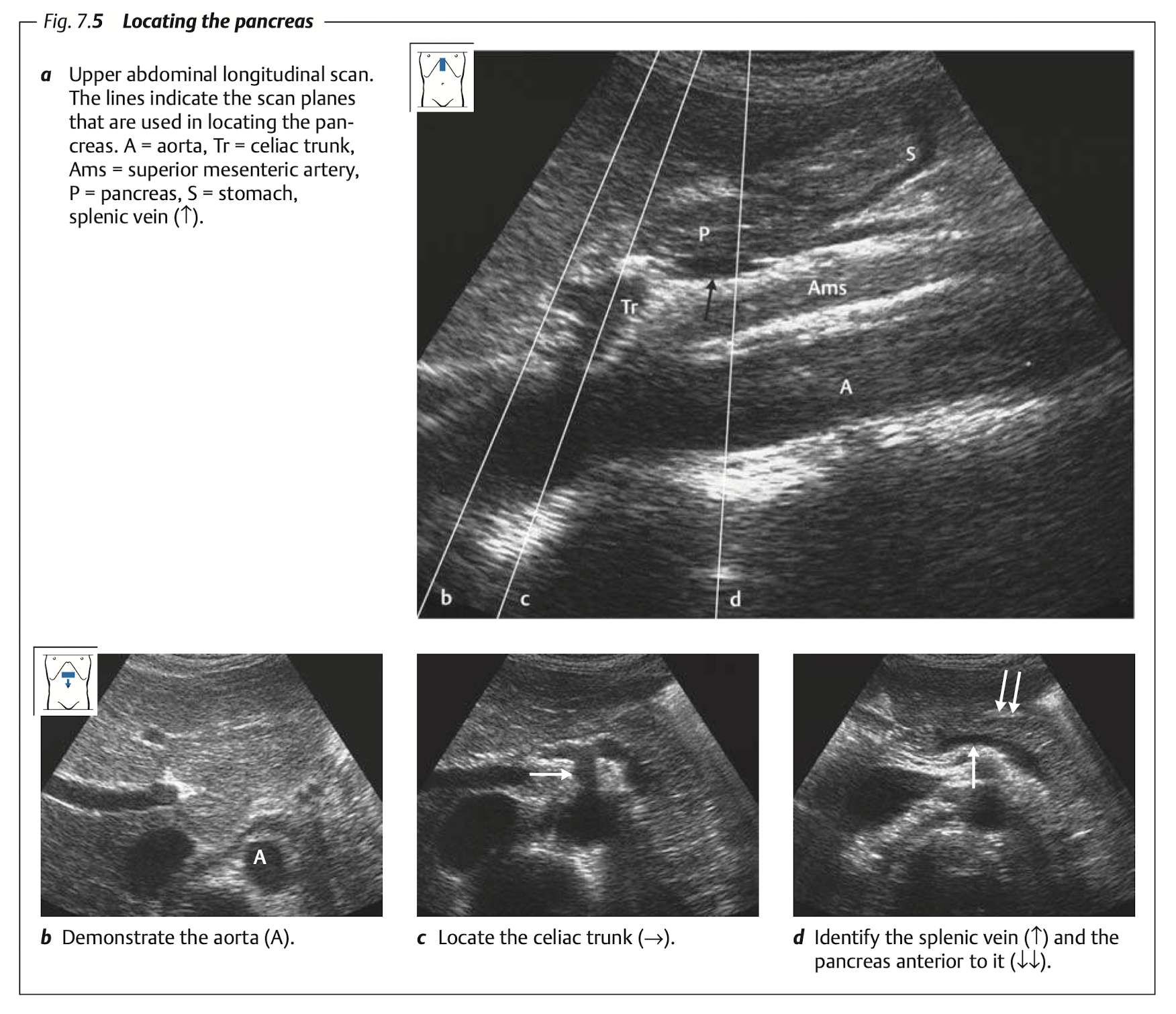
Pancreas
View
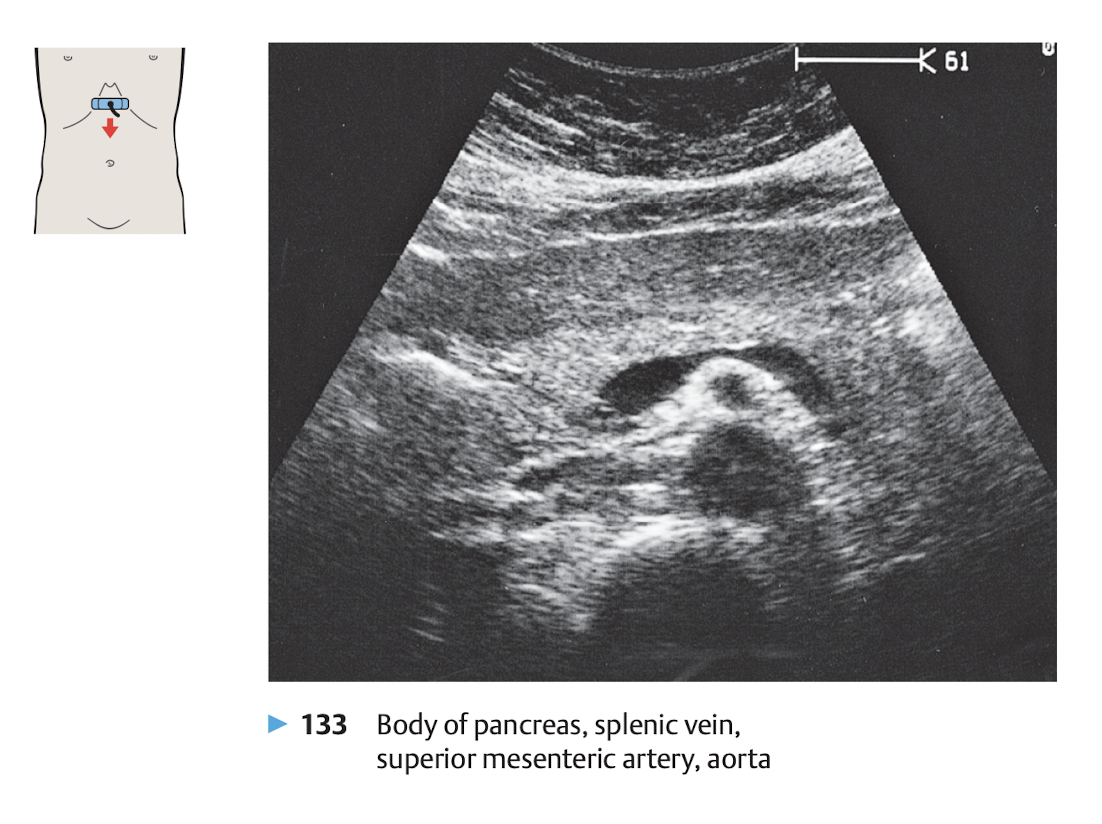
View: transverse view, angle the probe slightly upward to the liver.
use splenic vein as a land mark
The money shot of the pancrease is shown in Figure 11.
Finding pancreas
Tips
Pancrease is best examined in fasted patient.
If bowel gas obstruct the view, try:
Examine after the patient change position:
- From lateral decubitus to supine, or
- From supine to upright (sit).
Use acoustic windows:
Let the patient drink some water to fill in the stomach.
View through the liver.